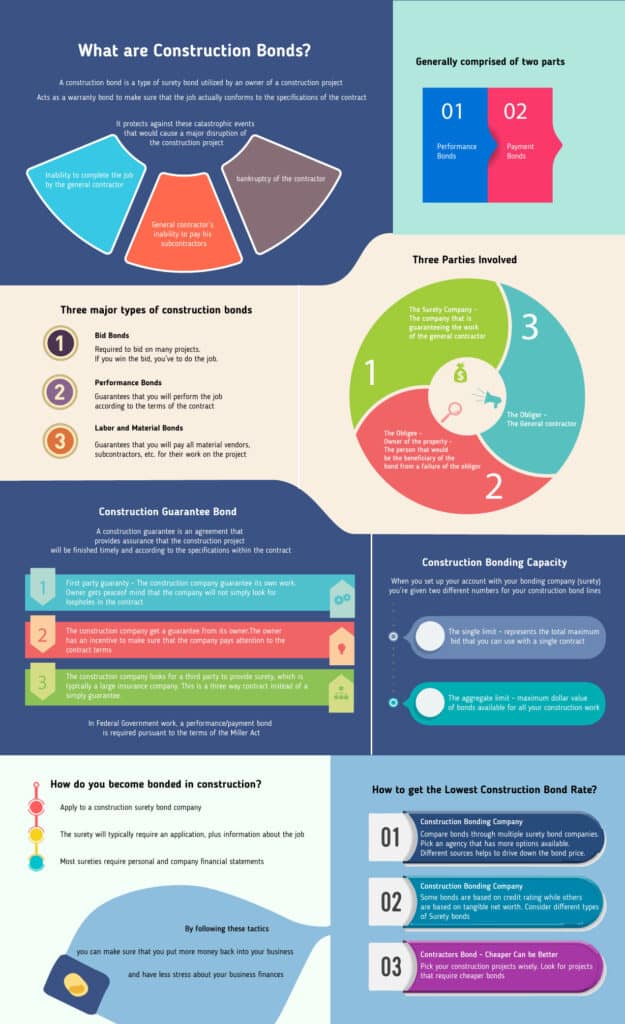
What are Construction Bonds?
The crux of why this sense of surety is so vital traces back to the core use of construction bonds. Infused with history, construction bonds, or contract bonds as they are often referred to, act as a safety net, protecting stakeholders from loss and ensuring steady cash flow throughout the construction process. These financial mechanisms, under the watchful eyes of underwriters, are subject to specific laws and state regulations. They date back to the rugged beginnings of the modern construction industry, with terms like Performance & Payment bonds being used interchangeably. A construction bond, typically issued by a surety company, is a pledge that safeguards the owner of a construction project from events or things that could pose a significant disruption to the construction project. These disruptions could include the general contractor‘s inability to complete the project, failure to pay subcontractors, or bankruptcy. These bonds also ensure that the construction work adheres to the detailed specifications laid out in the contract, effectively acting as a warranty for a full year after job completion.

Construction bonds, being a form of contract surety bonds, are not just an abstract concept but actively play a significant role in the way businesses operate. They provide protection to the obligee (project owner), the surety (bonding company), and the obligor (contractor). The function and responsibilities are explained with examples through an infographic, which works as a sort of table of contents, placing clear black and white text against a multicolored background. This is a symbolic representation of the myriad of roles and responsibilities that converge to bring a project to life and so remains an avenue of improvement in how we communicate complex ideas.
How Does a Construction Bond Work? Construction Bonds Explained
Taking a closer look at construction bonds reveals them as financial instruments that lend assurance, security, and protection. They forge connections among various parties such as investors, local states, and other stakeholders in a construction project. The involvement of professional entities like CPAs often aids in maintaining the transparency and accountability of these bonds, which is particularly crucial in providing financial security and assurance that construction projects will reach their successful completion.
- Issuance and Agreement:
- The contractor (principal) applies for the required construction bonds from a surety bonding company.
- The bonding company assesses the contractor’s financial stability, experience, and capacity to determine the risk involved in issuing the bonds.
- If approved, the bonding company issues the necessary bonds to the contractor.
- Bid Phase:
- Performance Bond:
- Once the contract is awarded to a contractor, a performance bond is typically required.
- The performance bond ensures that the contractor will complete the project according to the terms and conditions of the contract.
- If the contractor fails to fulfill its obligations, the project owner can make a claim against the performance bond to recover costs associated with hiring another contractor to complete the work.
- Payment Bond:
- A payment bond is often issued alongside the performance bond.
- The payment bond guarantees that subcontractors, suppliers, and laborers will be paid for their work and materials.
- If the contractor fails to make payments, parties with valid claims can make claims against the payment bond to recover the owed amounts.
- Maintenance Bond:
- In some cases, a maintenance bond (also known as a warranty bond) is required.
- The maintenance bond ensures that the completed project remains free from defects and issues during a specified warranty period.
- If defects arise within the warranty period, the project owner can make a claim against the maintenance bond to cover the cost of necessary repairs.
- Bond Claims:
- If a project owner or other stakeholders believe the contractor has defaulted or not fulfilled its obligations, they can file a bond claim with the bonding company.
- The bonding company investigates the claim to determine its validity and may ask for supporting documentation and evidence.
- If the claim is valid, the bonding company may compensate the claimant up to the bond’s coverage amount.
- Indemnity Agreement:
- Premiums and Costs:
A contract bond is a standard requirement in the construction sector, often referred to as a construction bond. If you hold an interest in unearthing more about this, you might want to visit our dedicated page with a detailed description of surety bonds.
A construction site, brought to life — the vibrant animation encapsulates the unyielding spirit, intricate processes, and the bond-fueled certainty underlying every construction project. As we close, it bears repeating how integral construction bonds are in ensuring the successful completion of these projects and effectively managing inherent industry risks. Contractors ought to familiarize themselves with the different types of bonds, their functions and the necessary steps to acquire and effectively leverage them. To successfully navigate the bond process, it is crucial to build relationships with experienced bonding companies and maintain robust financial stability.
Types of Construction Bonds for Construction Companies:
- Bid Bonds: A Bid bond is submitted by a contractor as part of the bidding process for a construction project. They serve as a guarantee that the contractor, if awarded the contract, shall enter into a contract and provide the necessary performance bond and payment (labor and material) bond. If the contractor backs out or fails to meet its obligations, the bid bond compensates the owner for the cost difference of awarding the contract to another bidder.
- Performance Bonds: A Performance bond provides assurance that a contractor will complete a project according to the terms and conditions specified in the contract. If that contractor defaults or fails to complete the work, then the bond ensures that the owner will be compensated regarding the cost of hiring another contractor to complete the project.
- Payment Bonds: Payment bonds protect material suppliers, subcontractors, and laborers by ensuring that they receive payment for their work and materials. If the general contractor fails to make payments, the payment bond allows the affected parties to make claims against the bond.
- Maintenance Bonds (Warranty Bonds): Maintenance bonds guarantee the quality of work and materials for a specified period after the project is completed. If defects or issues arise during the maintenance period, the bond covers the cost of necessary repairs.
Why Construction Bonds Are Important:
- Risk Mitigation: Construction projects involve various risks, including financial, performance, and payment risks. Bonds help mitigate these risks by providing financial security to project owners and ensuring that contractors fulfill their obligations.
 Trust and Credibility: Contractors with bonds demonstrate their financial stability and commitment to completing projects successfully. This enhances their reputation and credibility within the industry.
Trust and Credibility: Contractors with bonds demonstrate their financial stability and commitment to completing projects successfully. This enhances their reputation and credibility within the industry.- Legal and Contractual Requirements: Many public and private construction projects require contractors to obtain and maintain bonds as part of the contractual agreement.
Seven Steps for Contractors in Getting a Construction Bond:
- Preparation: Contractors should gather all necessary documentation, including financial statements, project details, and references, to demonstrate their qualifications and
financial stability.- Choose a Bonding Company: Contractors can work with surety bonding companies that assess their financial strength, experience, and bond capacity to determine the appropriate bonding limits and rates.
- Application Process: Contractors submit applications to bonding companies, providing detailed information about the project and their financials. The bonding company evaluates the application and may request additional information.
- Underwriting: The bonding company reviews the contractor’s credit history, financial statements, work history, and other relevant factors to assess the risk and determine bond terms.
- Bond Issuance: Once approved, the bonding company issues the required bonds to the contractor, who then provides them to the project owner.
- Project Execution: The contractor completes the project according to the contract terms. If any issues arise, the bonding company may get involved to ensure resolution.
- Bond Claims: If the contractor fails to fulfill their obligations, stakeholders can make claims against the bonds. The bonding company investigates the claim and may compensate the affected parties if the claim is valid.
Key Considerations for getting a Construction Surety Bond:
- Financial Stability: Contractors should maintain strong financial health to qualify for bonds and secure favorable terms.
- Contractual Understanding: Contractors must thoroughly understand the terms of the contract and their obligations before entering into a bond agreement.
- Selecting the Right Bonding Company: Contractors should choose a reputable and experienced bonding company that can provide appropriate guidance and support.
- Risk Management: Contractors should implement effective project management and risk mitigation strategies to reduce the likelihood of bond claims.
 The construction bond arrangement involves several parties, each with unique roles and responsibilities. However, the complexity of the construction project could necessitate the involvement of additional entities. It’s this arrangement that establishes a system of financial security and accountability, guaranteeing that the project is successfully concluded while offering protection from potential risks.
The construction bond arrangement involves several parties, each with unique roles and responsibilities. However, the complexity of the construction project could necessitate the involvement of additional entities. It’s this arrangement that establishes a system of financial security and accountability, guaranteeing that the project is successfully concluded while offering protection from potential risks.
Parties to a Construction Bond
Construction bonds involve several parties, each with specific roles and responsibilities. The main parties involved in a construction bond arrangement are:
- Principal (Contractor):
- The principal is the party seeking the bond (typically the contractor).
- The contractor applies for the bond and agrees to fulfill the terms and conditions of the bond agreement.
- The principal is financially responsible for reimbursing the bonding company in case a valid claim is paid out.
- Obligee (Project Owner or Beneficiary):
- The obligee is the party who requires the bond (usually the project owner).
- The obligee seeks financial protection and assurance that the principal will fulfill their contractual obligations.
- If the principal fails to meet its obligations, the obligee can make a claim against the bond to recover losses or damages.
- Surety (Bonding Company):
- The surety is the third party that issues the bond to the principal on behalf of the obligee.
- The surety assesses the principal’s financial stability, experience, and capacity to determine the risk involved in issuing the bond.
- If a valid claim is made against the bond, the surety investigates the claim and may compensate the obligee up to the bond’s coverage amount.
- The surety also has the right to seek reimbursement from the principal for any claim payouts.
- Subcontractors, Suppliers, and Laborers:
- These parties are not directly involved in the bond arrangement but can benefit from payment bonds.
- Payment bonds ensure that subcontractors, suppliers, and laborers receive payment for their work and materials, even if the general contractor defaults.
To summarize, contractors utilize surety bonds to fulfill project requirements, provide financial security, ensure payments to subcontractors and suppliers, improve their credibility, comply with legal and contractual obligations, and manage risks. With the right approach and the right team backing them, these bonds can significantly contribute to the success of a project. These bonds play a crucial role in fostering trust and accountability among all stakeholders, including the construction company, in a construction project. As a program of workmanship assurance, these bonds render assistance in ensuring all assigned tasks are suitably accomplished.
What do Construction Surety Bonds Cost?
We have a calculator that determines how much a construction bond costs, which you can find here: https://swiftbonds.com/performance-bond/cost/. This is super handy when you are getting your bid bond for a parking lot or similar construction projects. With the help of this tool, you can confidently build that amount into your bid for the lot.
By integrating these terms into the discussion, we can provide a more comprehensive overview of construction bonding and its various aspects in the construction industry.
- Bonding Construction: This term refers to the process of obtaining bonds for construction projects. It involves contractors working with bonding companies to secure the necessary bonds, such as bid bonds, performance bonds, and payment bonds, to fulfill contractual obligations.
- Bonding for Construction: This phrase is closely related to “Bonding Construction” and refers to the act of securing bonds for construction projects. Contractors seek bonding to reassure project owners and stakeholders that they have the financial stability and capability to complete the project as agreed.
- Construction Bonding Company: A construction bonding company is an entity that specializes in providing surety bonds to contractors. These companies evaluate the financial strength and experience of contractors and issue the appropriate bonds based on the project’s needs.
- Contractor Bonding Definition: This term pertains to the explanation or understanding of what contractor bonding entails. It involves the process of contractors obtaining bonds to guarantee their performance and fulfill contractual obligations.
- How Do Construction Bonds Work: This phrase directly addresses the mechanics of construction bonds. Construction bonds work by acting as a contract between the project owner, the contractor, and the surety. If the contractor fails to fulfill their obligations, the surety steps in to provide compensation to affected parties, ensuring the project’s continuity.
- What Do Construction Bonds Cover: This term concerns the scope of coverage provided by construction bonds. Construction bonds cover various aspects, including performance guarantees, payment to subcontractors and suppliers, and adherence to project specifications and timelines.
- Getting Bonded for Construction: This phrase refers to the process contractors undergo to secure bonds for construction projects. It involves meeting bonding requirements, working with bonding companies, and obtaining the necessary bonds to start or continue construction work.
- Project Bonding: Project bonding involves obtaining bonds specifically for a construction project. These bonds serve as a guarantee that the project will be completed as specified in the contract.
- Construction Surety Bond Example: This term refers to a real-world instance illustrating how a construction surety bond works. An example could showcase a scenario where a contractor defaults, and the surety steps in to cover the costs and ensure project completion.
- What Type of Bond Will Cover Construction Companies: This phrase addresses the specific types of bonds that are suitable for covering construction companies. As mentioned earlier, bid bonds, performance bonds, and payment bonds are the primary types used in the construction industry.
- Surety Bond Construction Industry: This term highlights the integral role of surety bonds within the construction industry. Surety bonds provide financial security, trust, and risk mitigation in construction projects.
- Surety Bond for Construction Project: This term emphasizes the application of surety bonds to individual construction projects. These bonds offer assurance to project owners that the contractor will meet their obligations.
